Medical Marijuana Options for Patients Suffering From Sciatica
What You Need To Know: Medical Cannabis for Sciatica
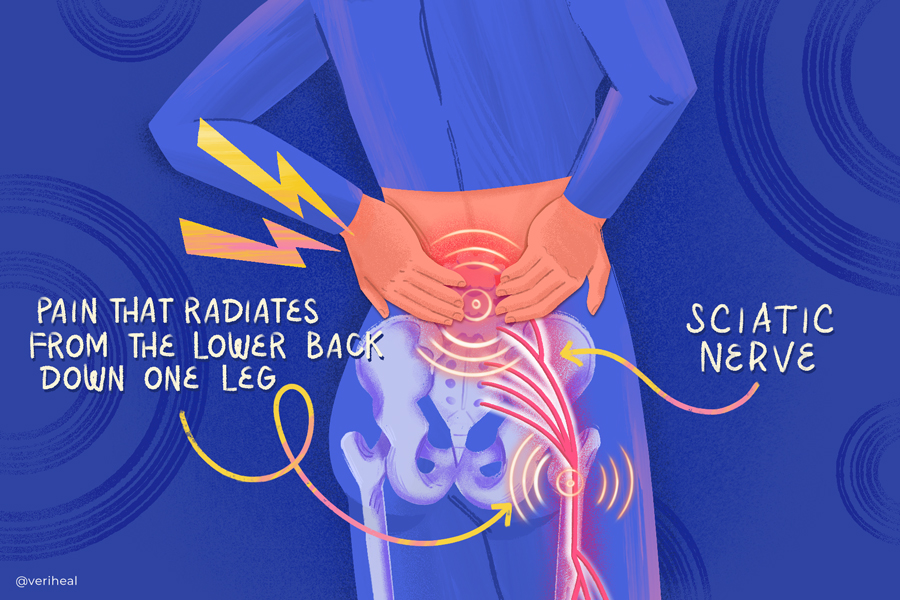
Sciatica is characterized by lower back pain radiating down the leg due to nerve compression. While conventional medications may not always provide relief, medical cannabis, targeting the endocannabinoid system, offers an alternative.
Cannabis components like THC and CBD act on cannabinoid receptors to:
- alleviate pain
- improve mood
- reduce neuropathy
- expand range of motion
Causes of sciatica vary from poor posture to spinal disorders, and complications can include herniated discs and nerve damage if left untreated. Medical cannabis, particularly CBD, presents a promising option with fewer side effects than traditional medications. However, it’s essential to consult a physician before considering any treatment.
The Science Behind Medical Cannabis for Sciatica:
- Why Use Medical Cannabis for Sciatica?
- Cannabis and Sciatica Recommendations
- Sciatica and Cannabis: What Research Shows
- What Is Sciatica?
- Causes of Sciatica
- Complications Caused by Sciatica
For many patients experiencing sciatica, nerve pain, numbness, and tingling in the lower back that radiates down the leg, can have heavy implications for completing daily activities. Sciatica pain occurs when the sciatic nerve is pinched or has pressure pushing up against it. Many patients try to find relief with over-the-counter pain medications or prescription medications like gabapentin and tricyclic antidepressants (7). Some patients do not see relief from their pain with these medications or opioids.
The first documented use of cannabis for sciatica was written by English physician Dr. William Salmon in 1710 (12). Since then, through years of research, scientists have discovered that cannabis is a great option for neuropathy or nerve symptoms that are caused by sciatica. Cannabis works by targeting the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS), which consists of fat-based neurotransmitters and cannabinoid receptors. The ECS is responsible for pain perception, maintaining homeostasis and proper body temperature, decreasing inflammation, and modulating the immune system.
Cannabis and its cannabinoids, including Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), affect the endocannabinoid system by targeting cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are in the central nervous system, including the spinal cord while CB2 receptors affect the peripheral nerves and a variety of organs. Various other receptors targeted by cannabinoids such as CBD may also contribute to pain relief, such as transient receptor potential (TRP) receptors.
One pathway of treating sciatic nerve pain with the endocannabinoid system is through CB1 receptors in portions of the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves that have the ability to modulate acute and persistent pain signals (18). Additionally, when CB1 and CB2 receptors are activated, amounts of the neurotransmitter anandamide (AEA) increase, causing astrocytes (a supportive and immunity type of brain cell) to release a protein that is thought to increase the growth of nerve cells and reduce inflammatory signals, nerve pain, numbness, and tingling sensations caused by sciatica (9).
For more information on how the endocannabinoid system works, please see our page on endocannabinoids here.
Why Use Medical Cannabis for Sciatica?
For those who are considering medical cannabis for relief of sciatica symptoms, you may also experience the following benefits (8):
- Decreased pain (17)
- Decreased neuropathy (18)
- Sleep improvements
- Improvements in mood and psychological distress, especially when it comes to anxiety or depression (17)
- Decreased fatigue
Adverse side effects from medical cannabis treatment include somnolence, sedation, confusion, tachycardia or increased heart rate, dry mouth, and psychosis (8).
Cannabis and Sciatica Recommendations
Clinical guidelines suggest that cannabis should be considered a third to fourth-line treatment option for pain management if other medications have not improved nerve symptoms (8). For more specific information about treating sciatica, including numbness, tingling, and nerve pain, please check out our guide on neuropathy or our guide on back pain. Additionally, our page on chronic pain details how to begin medical marijuana treatment, which acts as an analgesic, or pain reliever. Typically it is recommended to begin with smaller doses until you know what’s right for you.
Before beginning any medical treatment, and before stopping any currently existing medications, you should consult with your doctor and make sure you have their approval. It’s important, especially when going off a medication you might be currently taking, to have a doctor’s supervision. But with the help of your physician, you may find that cannabis is the pain management tool you’ve been looking for to help you manage sciatica and other nerve pain issues.
CBD for Sciatic Nerve Pain
Many patients with sciatica, a type of radicular pain because of how it radiates to different parts of the body, also see benefits from using CBD products only. CBD is known for its ability to reduce inflammation through transient receptor potential (TRP) receptors of the body. It also does not cause psychoactive effects like THC. Patients using CBD for sciatica may see benefits from topical products such as creams or CBD oils which can be taken orally as well. Check out our arthritis page for more information on how to utilize CBD as a painkiller.
Sciatica and Cannabis: What Research Shows
A 2016 study in the International Journal of Anesthesiology & Pain Medicine examined the effects of medical cannabis on patients with sciatica, spinal stenosis, and herniated discs. These patients failed at least two narcotic drugs and tried 12 months of conventional treatment before the trial began (19). The study followed patients with imagable causes of sciatica for 12 months and evaluated patients for pain and range of motion.
Because this study followed patients for an extended period, it has provided a good analysis of the effects of medical cannabis on patients with sciatica and lower back pain. The results of the study show that these patients experienced an increase in range of motion, along with increased mental function and a decrease in back pain.
A 2018 study examined the effects of cannabis on 15 men suffering from chronic nerve pain. Nine of the men were given an average of 15 milligrams of sublingual THC every six hours. The other six men in the study were given placebos. Before the treatments were administered, the participants rated their pain level at an average of 53 out of 100, with 100 being the highest and zero representing no pain (17). After the treatment, the participants who had received THC reported their pain decreasing to an average of 35. Those who were given placebos reported an average pain level of 43—enough of a difference to indicate that the THC did have an effect.
Not only did these results show a strong argument for medical marijuana use in patients with neuropathy and sciatica, but it also showed that two areas of the brain, the anterior cingulate cortex and the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, are involved in pain relief (17). Because of this, the researchers of the study believe that THC may actually help rebuild pain connectivity channels that have been damaged from having chronic pain.
In addition, a 2018 Cochrane Library review also shows promising results for utilizing cannabis for chronic neuropathic, or nerve pain in adults. This review of 16 studies and 1750 participants concluded that a significantly larger number of patients who received cannabis saw 50% or greater improvement of pain relief (8). This information is promising and calls for more research with longer study windows to determine how effective cannabis treatment is overall for different types of nerve pain.
What Is Sciatica?
The sciatic nerve begins in the lower back and travels through the hips and buttocks and down each leg. When part of the nerve is compressed, often as a result of a herniated disc, bone spur, or narrowing of the spine, pain radiates down the nerve. This pain can be moderate to severe. Most sciatica patients experience pain on only one side of the body, though it is possible to experience it on both sides.
Traditional anti-inflammatory and muscle relaxing medications are often used to treat sciatica. But when the pain caused by the condition is severe, doctors may prescribe narcotics or opioids to help manage it. Side effects of opioid use include dependence and fatal overdose, neither of which is a serious concern when it comes to cannabis use.
Causes of Sciatica
There are several causes of sciatica, which is nerve pain that often radiates from the lower back down into the leg and sometimes in the foot. The symptoms of sciatica are typically caused when there is pressure against the sciatic nerve, which is a major nerve in your lower back that runs down the legs. Some of the causes of sciatic pain include (15):
- Poor posture
- Awkward sitting positions
- A tumor pressing against the sciatic nerve
- A spinal abscess (3)
- Obesity
- Blood clot
- Herniated or bulging disc in the spine (14)
- Spinal stenosis (14)
- Injuries such as a pelvic fracture (14)
- Lower back or pelvic muscle spasms and inflammation (3)
- Nerve disorders that include (11):
Complications Caused by Sciatica
In some cases, sciatica can be much more than nerve pain, tingling, and numbness down a leg. Complications from sciatica or other serious underlying conditions can develop over time if the pressure on the sciatic nerve is not released. These complications may include (15):
- Increased pain
- Slipped or herniated disc
- Loss of feeling or weakness of the affected leg
- Loss of bowel or bladder function
- Permanent nerve damage
Note: Veriheal does not intend to give this as professional medical advice. Do not attempt to self-diagnose, or prescribe treatment based on the information provided on this page. Always consult a physician before making any decision on the treatment of a medical condition.
1. Calignano, A., La Rana, G., Giuffrida, A., & Piomelli, D. (1998). Control of pain initiation by endogenous cannabinoids. Nature, 394(6690), 277–281. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9685157/
2. Costa, B., Trovato, A. E., Colleoni, M., Giagnoni, G., Zarini, E., & Croci, T. (2005). Effect of the CANNABINOID Cb1 receptor antagonist, Sr141716, on nociceptive response and nerve demyelination in rodents with CHRONIC constriction injury of the sciatic nerve. Pain, 116(1), 52-61. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S030439590500151X
3. Davis, D., Kushagra, M., & Vasudevan, A. (2021, February 26). Sciatica. Retrieved March 28, 2021, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507908/
4. First, L., Douglas, W., Habibi, B., Singh, J. R., & Sein, M. T. (2020). Cannabis use and low-back pain: A systematic review. Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research, 5(4), 283-289. https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/10.1089/can.2019.0077
5. Hohmann, A., & Herkenham, M. (1999). Cannabinoid receptors undergo axonal flow in sensory nerves. Neuroscience, 92(4), 1171-1175. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0306452299002201
6. Keppel Hesselink, J. M., & Kopsky, D. J. (2015). Palmitoylethanolamide, a neutraceutical, in nerve compression syndromes: efficacy and safety in sciatic pain and carpal tunnel syndrome. Journal of pain research, 8, 729–734. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4631430/
7. Moley, P., MD, & P. (2020, November). Sciatica – musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders. Retrieved March 28, 2021, from https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/musculoskeletal-and-connective-tissue-disorders/neck-and-back-pain/sciatica
8. Mücke, M., Phillips, T., Radbruch, L., Petzke, F., & Häuser, W. (2018). Cannabis-based medicines for chronic neuropathic pain in adults. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews, 3(3), CD012182. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6494210/
9. Nagarkatti, P., Pandey, R., Rieder, S. A., Hegde, V. L., & Nagarkatti, M. (2009). Cannabinoids as novel anti-inflammatory drugs. Future medicinal chemistry, 1(7), 1333–1349. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2828614/
10. Nerve pain in the Legs? Medical marijuana may alter Brain Connections, bring relief. (n.d.). Retrieved March 28, 2021, from https://www.aan.com/PressRoom/Home/PressRelease/1669
11. Neurological disorders. Johns Hopkins Medicine. (n.d.). Retrieved January 8, 2022, from https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/neurological-disorders
12. Ryz, N. R., Remillard, D. J., & Russo, E. B. (2017). Cannabis roots: A traditional therapy with future potential for treating inflammation and pain. Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research, 2(1), 210–216. https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/10.1089/can.2017.0028
13. Santos, G. X., De-Souza, G. G., Alves, S. S., Ocamoto, G. N., Parizotto, N. A., & Dos-Reis, L. M. (2020). The influence of the cannabinoid Receptor CB1 on the periaqueductal gray in mice treated WITH Photobiomodulation after CHRONIC constriction injury of the SCIATIC nerve: A placebo-controlled trial. Brazilian Journal Of Pain, 3(1). https://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?pid=S2595-31922020000100002&script=sci_arttext
14. Sciatica. (2020, December 16). Retrieved March 28, 2021, from https://medlineplus.gov/sciatica.html
15. Sciatica. (n.d.). Retrieved March 28, 2021, from https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/sciatica
16. Seltzman, H. H., Shiner, C., Hirt, E. E., Gilliam, A. F., Thomas, B. F., Maitra, R., . . . Spigelman, I. (2016). Peripherally selective cannabinoid 1 receptor (cb1r) agonists for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 59(16), 7525-7543. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00516
17. Weizman, L., Dayan, L., Brill, S., Nahman-Averbuch, H., Hendler, T., Jacob, G., & Sharon, H. (2018). Cannabis analgesia in chronic neuropathic pain is associated with altered brain connectivity. Neurology, 91(14). https://n.neurology.org/content/91/14/e1285
18. Wilsey, B., Marcotte, T., Tsodikov, A., Millman, J., Bentley, H., Gouaux, B., & Fishman, S. (2008). A randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial of cannabis cigarettes in neuropathic pain. The journal of pain, 9(6), 506–521. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4968043/
19. Yassin, M., Garti, A., & Robinson, D. (2016, November 29). Effect of medicinal cannabis therapy (mct) on severity of chronic low back pain, sciatica and lumbar range of motion. Retrieved March 28, 2021, from https://anaesthesia-painmedicine.imedpub.com/effect-of-medicinal-cannabis-therapy-mct-on-severity-of-chronic-low-backpain–sciatica-and-lumbar-range-of-motion.php?aid=17737
20. Reiman, A., Welty, M., & Solomon, P. (2017). Cannabis as a substitute for opioid-based pain medication: Patient self-report. Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research, 2(1), 160–166. https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/10.1089/can.2017.0012








